Industrial Control Systems Security Checklist
Cyberattacks on industrial control systems (ICS) aren’t just something you read about in news headlines anymore—they’re happening all around us, and they're getting worse. In 2024, ransomware attacks jumped by a staggering 87%. That’s not just a number—it’s a wake-up call. For four years straight, critical infrastructure has been under fire, and the danger keeps growing.
The world got its first real shock back in 2010 with Stuxnet. It wasn’t just another virus—it was a game-changer. That tiny piece of code quietly sabotaged Iran’s nuclear centrifuges, damaging them while pretending everything was fine on the monitors. It was silent, invisible, and terrifyingly effective. Fast forward to 2015, and the people of Ukraine found themselves suddenly in the dark—literally. Russian-linked hackers took down the power grid, leaving 230,000 homes without electricity in the middle of winter. These weren’t just technical failures—they were human disasters.
- ICS systems are under serious threat. Hackers—from cybercriminals to nation-states—are becoming more aggressive and more advanced.
- Old systems are vulnerable. Many industrial setups still rely on outdated technology, and when you mix those with modern IT systems, it opens the door to attack.
- This is about more than data. These hacks can cause real-world harm—power outages, broken machinery, even threats to human life. It's not just about protecting data anymore; it’s about safety and keeping things running.
- Ransomware hits where it hurts. Downtime in industrial environments is expensive and dangerous, and hackers know it. That’s why attacks on these sectors are so profitable for them.
- We need strong defenses. Protecting ICS requires more than just firewalls. It calls for experts who understand operational technology (OT), a solid plan for bouncing back, and closing the gap between IT and OT teams.
Breaking the Air Gap
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) were once thought to be untouchable—sealed off, isolated, and secure behind air gaps. These systems run the critical things that keep our world going: water pumps, power grids, factory machines. For years, the belief was simple: if these systems weren’t connected to the internet, they couldn’t be hacked.
But that time is over.
As technology moves forward and more systems become connected, that protective isolation is breaking down. ICS setups are now vulnerable in ways they never were before. Cybercriminals and even nation-state attackers have realized that if they can compromise these systems, they can cause real, physical damage. We're no longer talking about data theft—we’re talking about turning off the lights, stopping production lines, or disrupting entire cities. The stakes have never been higher.
Nation-State Actors and APTs
Behind many of these attacks are highly skilled teams—often backed by governments—who don’t just go after systems randomly. They plan, they wait, and they strike with precision. These are known as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), and they operate like digital spies, slipping into systems quietly and staying hidden for months—or even years.
Countries like Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea have been tied to these kinds of operations. Each uses its own playbook: some send carefully crafted phishing emails to engineers, others scan for vulnerable industrial devices that haven't been updated. What they all have in common is patience and expertise. They're not looking for a quick payday—they're here to infiltrate, observe, and sometimes even destroy.
It’s a chilling thought: these groups aren’t stealing credit card numbers—they’re probing the backbone of modern civilization.
The Ransomware Revolution Targeting Critical Infrastructure
On another front, financially motivated cybercriminals are going after ICS and OT (Operational Technology) environments with relentless force. They’ve realized these systems are often outdated, under-protected, and incredibly valuable targets.
Take the 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack—it started with something as small as a stolen VPN password. That single weak point caused fuel shortages and price hikes across the eastern U.S. The hackers didn’t even touch the pipeline systems directly. Instead, they exploited the weak connections between IT and OT systems, and the whole thing spiraled out of control.
Now, ransomware attacks are everywhere, and industrial sectors are especially tempting. Why? Because downtime in these industries is outrageously expensive. Companies can’t afford to sit idle, so they often pay the ransom just to get back online.
According to a 2023 Chainalysis report, ransomware gangs pulled in over $1 billion in cryptocurrency last year—an all-time record. A huge chunk of that came from industries we all rely on: power, water, transportation, and manufacturing.
Groups like LockBit, Cl0p, Black Basta, and the now-disbanded Conti know this. They’re going after companies that can’t afford even a few hours of disruption. Imagine a car manufacturer losing $2.3 million every single hour the line is down. The pressure to pay is overwhelming.
Meanwhile, these cybercriminals are getting more advanced. They’re building malware tailored specifically for ICS and OT systems—malware that doesn’t just lock files but can stop machines, trigger malfunctions, or shut down entire facilities.
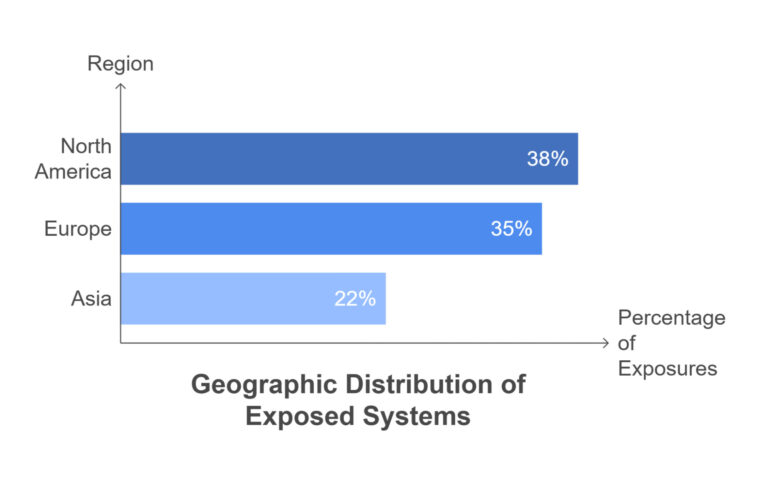
What’s even more worrying? There are over 145,000 industrial systems currently exposed online—and nearly 50,000 of those are in the U.S. alone. That’s tens of thousands of digital doors left cracked open.
The Hidden Weak Spots in Industrial Systems
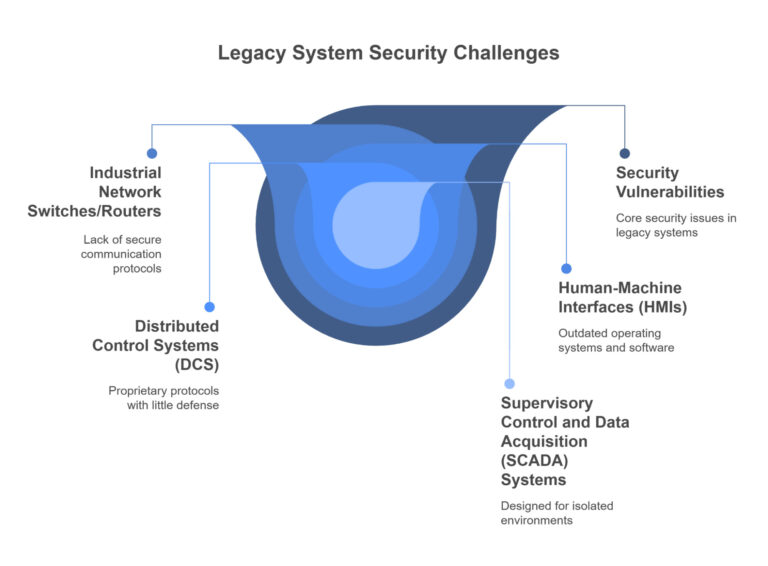
Why are industrial systems so vulnerable to cyber threats? The truth lies in how they were originally built—with a focus on performance and reliability, not security. These systems are often decades old, yet they still control some of the most critical infrastructure in the world today.
Unlike typical IT networks, industrial environments weren’t designed to face modern cyber threats. Their unique setup opens doors for attackers, and unfortunately, those doors are often left unlocked.
How Hackers Quietly Infiltrate ICS Environments
When hackers break into Industrial Control Systems (ICS), they don’t usually make a scene. Instead, they stay quiet, learning the system from the inside—sometimes for months—before making a move.
Take the 2015 cyberattack on Ukraine’s power grid. Hackers patiently explored the system for over half a year, collecting passwords and studying how everything worked. When they finally struck, they targeted the most sensitive parts: SCADA systems, Human-Machine Interfaces, and remote units that controlled the circuit breakers. The result? Widespread power outages and chaos.
This kind of attack isn’t about quick destruction. It’s about patience and precision—a chilling reminder of how vulnerable these systems really are.
Old Systems, Big Problems
Walk into many industrial plants today, and you might feel like you’ve stepped back in time. That’s because a lot of these facilities still rely on equipment from the 1980s or 90s—technology that was never meant to face the cybersecurity threats of today.
One real-life example: a major U.S. water utility still uses a control system from the early 1990s. Its core computer runs on Windows XP—an operating system that Microsoft stopped supporting over a decade ago. Why hasn’t it been replaced? Because upgrading would cost millions and require shutting down vital services. So, they keep running it, even though it’s full of known security holes.
And this isn’t a rare case. According to a 2023 survey by Claroty, over 60% of utilities still run their operations on outdated, unsupported systems. It’s a ticking time bomb—and everyone knows it.
IT vs. OT Security: A Different Kind of Battle
When it comes to cybersecurity, protecting industrial systems (OT – Operational Technology) is a completely different game compared to traditional IT. The stakes are much higher—not just stolen data or locked files, but real-life consequences like power outages, damaged equipment, or even explosions.
IT teams mostly focus on protecting data. But in an industrial setting, we’re talking about keeping factories running, water flowing, and power grids stable. A cyberattack here doesn’t just mess with computers—it can shut down critical services people rely on every day.
The challenge is, a lot of these systems were built years ago—long before cyber threats were even a thing. They weren’t designed with security in mind, so basic protections like encryption or authentication are often missing. And yet, they’re expected to run 24/7 without interruption.
Protecting these environments isn’t just about tech skills—it’s about knowing how these systems work in the real world. You need to understand the industrial processes, the flow of production, and the physical risks involved. Because in OT, one bad command or a single wrong signal can lead to serious, even life-threatening consequences.
Here, cybersecurity isn’t just about defense—it’s about keeping people safe and operations running no matter what.
Protection and Response: You Need Both
Let’s be honest: no system is ever 100% secure, especially when you’re dealing with decades-old equipment and environments that can’t just be patched or shut down for updates. That’s why the smartest approach today isn’t just about building strong walls—it’s also about planning what to do when someone climbs over them.
Layered Defenses and Better Visibility
According to a 2023 SANS ICS Cyber Security Survey, two of the most effective ways to cut down cyber risk in OT environments are network segmentation and continuous monitoring. That means breaking your network into secure zones and keeping an eye on everything, all the time.
Trying to treat OT security the same way we treat IT security is a big mistake. A lot of traditional IT tools just aren’t built for the industrial world. They don’t understand the language these machines speak, and sometimes they even make things worse by causing disruptions.
Industrial systems are complex, and they deserve security tools made for their unique challenges—not generic solutions.
Building Real-World Resilience
Let’s face it—attacks will happen. So, while it’s still important to prevent them, it’s just as important to prepare for impact.
That means designing systems that can take a hit without falling apart—and having teams ready to respond quickly and confidently when something goes wrong. It's about bouncing back fast and staying safe in the process.
One of the most effective ways to do that? Practice. Run cyberattack drills. Simulate incidents. Stress-test your systems and your teams. It’s better to find your weak spots on a calm Tuesday afternoon than in the middle of a real crisis at 2 AM when the phones won’t stop ringing.
Here are a few examples:
- Water utilities should practice what to do if someone tampers with the chemical dosing system.
- Power companies should simulate a scenario where someone takes over part of a substation.
- Factories should test how they’d react if someone tried to quietly mess with product quality.
Your system architecture should also include fail-safes and manual overrides—ways to keep critical operations running even when the digital side is under attack.
The old idea of “security by design” is no longer enough. Today, we also need resilience by design—building systems that can operate safely even when something goes wrong.
As Jen Easterly from CISA puts it:
“We need to assume breaches will happen and design systems that can continue safe operation even when compromised.”
The Bottom Line
Cyberattacks on industrial systems are getting more frequent and more dangerous—often backed by nation-states who want to cause disruption, not make money.
One of the biggest problems? A disconnect between IT and OT teams. Engineers often don’t think much about cybersecurity, and IT folks don’t always understand how the industrial systems work. That gap can leave serious blind spots.
Closing it means building bridges between teams, segmenting OT networks, and giving people targeted training so they understand both the risks and the tools to manage them.
As technologies like Industrial IoT, cloud computing, and AI become more common, they bring amazing benefits—but also new risks. That’s why having strong baseline security standards isn’t just a best practice anymore—it’s essential to keep our critical infrastructure safe from becoming the next headline.
- Dragos 2025 OT Cybersecurity Report A Year in Review (Hub Dragos)
- ODNI 2025 Threat Assessment notes threats from Russia, China, Iran, North Korea targeting critical infrastructure, telecom (Industrial Cyber)
- Ransomware Hit $1 Billion in 2023 (Chainalysis)
- The True Cost of Downtime 2024 (Siemens)
- NThe 2024 State of the Internet Report (Censys)
- Report: The Global State of Industrial Cybersecurity 2023 (Claroty)
- SANS ICS/OT Cybersecurity Survey: 2023’s Challenges and Tomorrow’s Defenses (RMC Global)

%20(24).jpg)